Discover everything about medical fitness — benefits, programs, chronic disease prevention, exercise prescriptions, and steps to achieve long-term health.
Medical Fitness: The Complete Guide
Medical fitness is no longer a niche topic — it’s the bridge between modern medicine, exercise science, and long-term wellness. Whether you’re recovering from a chronic condition, trying to prevent future health risks, or simply seeking a safe, supervised approach to fitness, medical fitness offers a personalized roadmap to sustainable health.
In this complete guide, you’ll learn:
-
What medical fitness really means and why it matters
-
How medically supervised programs reduce risk and improve outcomes
-
Key steps to build a personalized exercise prescription
-
How clinical exercise centers differ from regular gyms
-
Practical things you must do to achieve medical fitness safely
-
FAQs and actionable How-To strategies you can use immediately
What Is Medical Fitness?
Medical fitness is an evidence-based approach to exercise and wellness that helps prevent, manage, or even improve chronic conditions with professional supervision. Unlike standard workout programs, these centers use qualified staff, thorough assessments, and structured exercise plans to ensure safety and better results.
Key elements include:
-
Comprehensive health evaluations before starting any exercise
-
Collaboration among physicians, exercise specialists, and therapists
-
Personalized programs for specific needs such as heart health, diabetes control, or weight management
-
Lifestyle guidance combined with nutrition and behavioral support
-
Ongoing oversight to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments
For a broad definition, check the Medical Fitness Association.
Why Medical Fitness Matters in Today’s World
Modern lifestyles have made sedentary habits and chronic diseases common. Heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, and obesity are now leading global health threats. Traditional gyms and boot camps aren’t designed for people who need exercise therapy instead of just exercise intensity.
Medical fitness provides:
-
Reduced injury risk through careful screening and monitoring
-
Faster recovery after illness or surgery
-
Better disease prevention outcomes backed by research
-
A safe environment for high-risk individuals who may not tolerate conventional workouts
Learn more about preventive fitness programs in our article “7-Day Fitness Plan for Beginners”
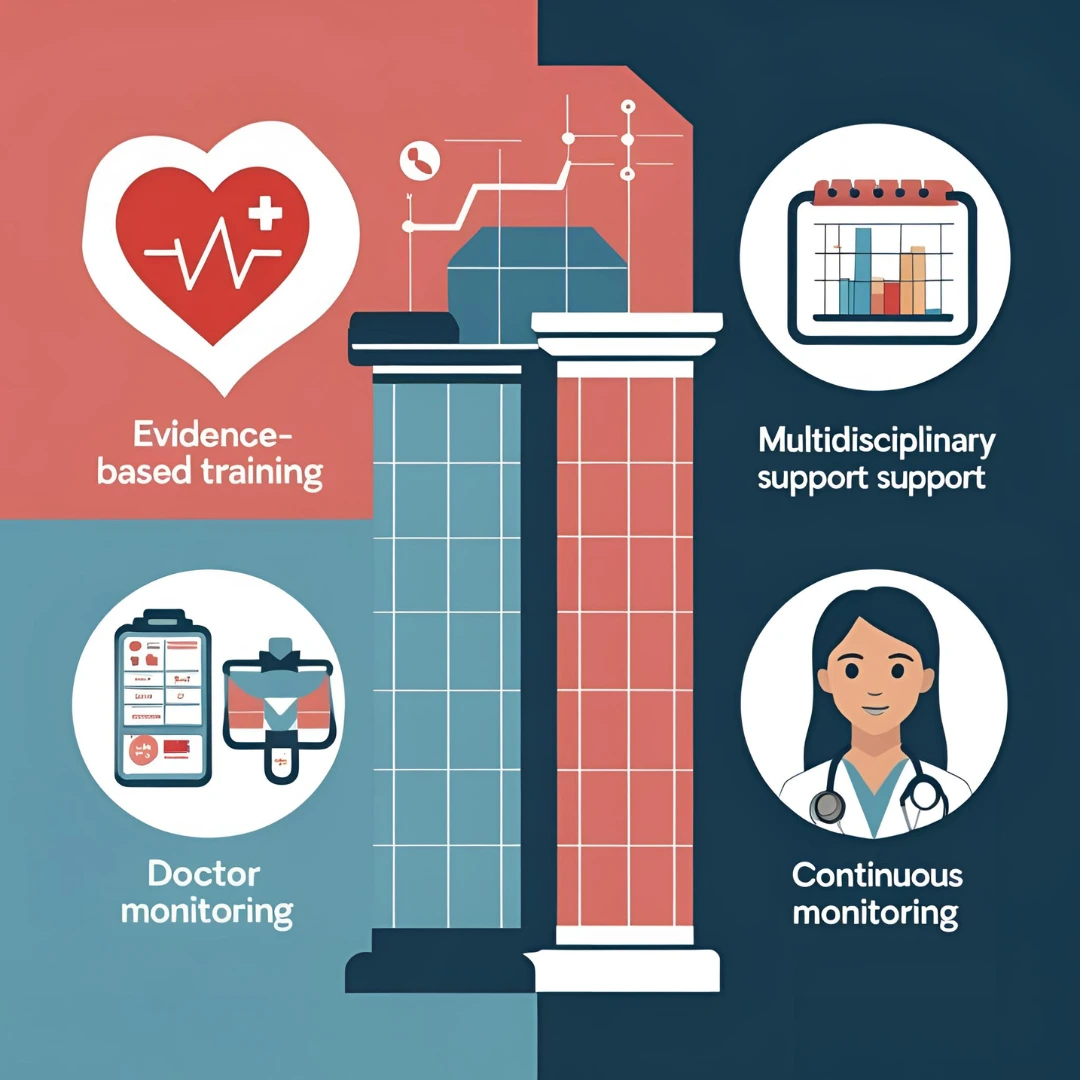
The Core Principles of Medical Fitness
1. Evidence-Based Exercise Prescription
Every client undergoes clinical screening — blood pressure checks, glucose testing, body composition analysis — before an exercise plan is created. The program is adjusted to match medical conditions, age, and physical capacity.
2. Multidisciplinary Support
Physicians, physical therapists, and certified trainers work as a team to design programs that improve mobility, cardiovascular health, strength, and flexibility without overloading the body.
3. Continuous Progress Monitoring
Unlike regular gyms, clinical exercise program centers track biomarkers and performance indicators at every stage. This ensures programs stay aligned with your health status.
4. Focus on Long-Term Lifestyle Change
Health based fitness is not about quick fixes or extreme routines. It integrates healthy habits that are sustainable for life.
Benefits of Medical Fitness Over Traditional Training
-
Personal safety: All workouts are medically supervised.
-
Better results: Programs are tailored to your body and condition.
-
Comprehensive care: Includes lifestyle coaching and clinical oversight.
-
Insurance partnerships: Some programs are covered by health plans.
-
Disease management: Ideal for cardiac rehab, arthritis, diabetes, or obesity.
See more about structured programs at Premise Health’s medical fitness management.

Medical/Clinical Fitness Programs: Types and Structure
Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
For patients recovering from heart attacks, angioplasty, or bypass surgery. Includes low-intensity monitored workouts, nutrition counseling, and stress management techniques.
Diabetes and Metabolic Control
Specialized routines to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar, often combined with diet planning and weight-loss counseling.
Orthopedic and Post-Surgical Recovery
Designed to restore mobility, flexibility, and strength after joint replacement, ligament surgery, or chronic pain therapy.
Preventive Medical Fitness
Not just for patients — healthy adults also benefit from programs that lower future risk of chronic disease.
See our article “Best Exercises for Preventive Health” for home-based workouts.

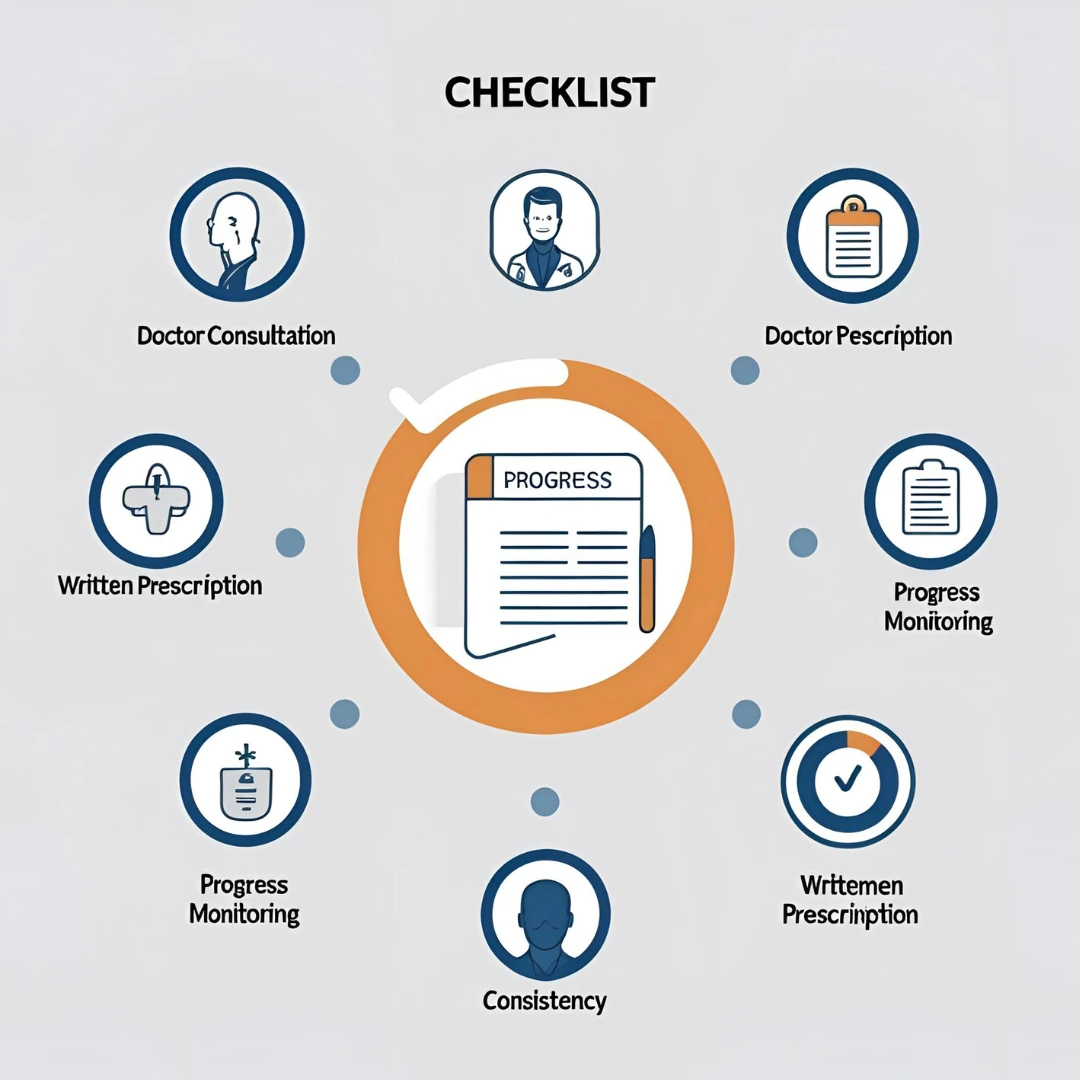
Things You Must Do to Achieve Medical/Clinical Fitness
Step 1. Get a Professional Health Assessment
Clinical fitness always starts with testing. Have your doctor evaluate cardiovascular health, joint function, and metabolic markers before joining a program.
Step 2. Choose the Right Medical Fitness Facility
Look for centers that are certified by the Medical Fitness Association (MFA) or employ licensed clinical staff.
Step 3. Follow Your Exercise Prescription Exactly
Consistency is key. Clinical fitness programs are designed to work in gradual, safe increments. Avoid skipping or modifying routines on your own.
Step 4. Track Your Progress With Data
Use fitness trackers or center-provided monitoring to see blood pressure, glucose, weight, and strength gains.
Step 5. Combine Exercise With Lifestyle Changes
No amount of exercise can outdo poor nutrition or lack of sleep. Pair clinical workouts with diet planning and stress management.
How to Start a Medical Fitness Program (Actionable Guide)
Beginning a Clinical fitness program is not like joining a regular gym. It’s a structured, clinically guided approach to improving health, preventing disease, and enhancing long-term performance. Follow these steps to start the right way:
1. Consult Your Physician for Clearance
Before starting, get a medical evaluation to ensure you can exercise safely. This is especially important if you have existing conditions or are new to structured training.
2. Choose the Right Medical Fitness Center
Look for certified facilities that focus on supervised programs rather than unsupervised workouts. You can also explore structured training plans such as this 6-day gym workout schedule to complement your clinical fitness program.
3. Request a Health Risk Assessment
A true Clinical fitness program always begins with a comprehensive assessment — including blood pressure, cardiovascular screening, and movement analysis — to create a safe baseline for your training.
4. Get a Personalized Exercise Prescription
Your program should outline how often to train, what exercises to perform, and how to progress over time. If you’re interested in building strength alongside medical guidance, this beginner calisthenics guide shows how structured progression works.
5. Set Measurable and Realistic Goals
Whether your goal is improving heart health, managing weight, or recovering from injury, define metrics that track your progress clearly.
6. Schedule Regular Progress Reviews
Meet with your Clinical fitness specialist every few weeks to adjust your plan. Consistent review keeps your program safe and effective. You can also see how targeted programs like this 7-day protein diet plan for weight loss can align with clinical fitness goals.
7. Stay Consistent and Build a Routine
Commit to two to four supervised sessions per week and reinforce them with healthy nutrition, recovery, and lifestyle habits.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

Q: What is the difference between a gym and a Medical / Clinical fitness center?
A: A traditional gym focuses on general workouts and physical fitness, while a clinically integrated fitness program provides evidence-based exercise plans designed for specific health needs. These include thorough assessments, professional oversight, and progress tracking to ensure safety and measurable results.
Q: Is medical / clinical fitness only for people with chronic diseases?
A: No. Therapeutic exercise programs also benefit healthy individuals by offering preventive screening, personalized workout prescriptions, and lifestyle coaching to maintain wellness and reduce future health risks.
Q: How do I know if a medical / clinical fitness program is legitimate?
A: Look for centers that are Medical / clinical Fitness Association (MFA) certified or employ clinical exercise physiologists, licensed therapists, or other healthcare-trained professionals. These credentials guarantee the program follows strict standards and integrates medical care effectively.
Q: Can medical / clinical fitness help with weight loss?
A: Yes. Medically / clinically supervised workout plans are tailored to metabolic health, body composition, and long-term sustainability. They outperform generic gym-based weight-loss plans by focusing on safe fat reduction, muscle balance, and lifestyle changes that last.
Conclusion: The Future of Fitness Is Medical
Medical fitness is no longer just a buzzword — it’s the next evolution in healthcare and exercise science. By integrating clinical oversight, individualized training, and evidence-based wellness plans, clinically supervised fitness programs give people of all ages — from athletes to those managing chronic conditions — a safer, more effective way to stay healthy.

If you’re working toward structured fitness goals, combining physician-guided training with traditional workout strategies can maximize your results. For example, a well-planned 6-day gym workout schedule can be adapted within a medically integrated exercise program to ensure every workout supports your long-term health.
Whether you want to prevent disease, recover faster, or simply train smarter, clinical exercise programs ensure every session is tailored to your body, your goals, and your medical profile.
The takeaway? Medical fitness isn’t optional anymore — it’s essential. When you choose therapeutic fitness programs, you’re not just exercising — you’re investing in a healthier, longer, and more active life backed by science and clinical expertise.


2 thoughts on “Medical Fitness: The Complete Guide to Health-Focused Training 2025”